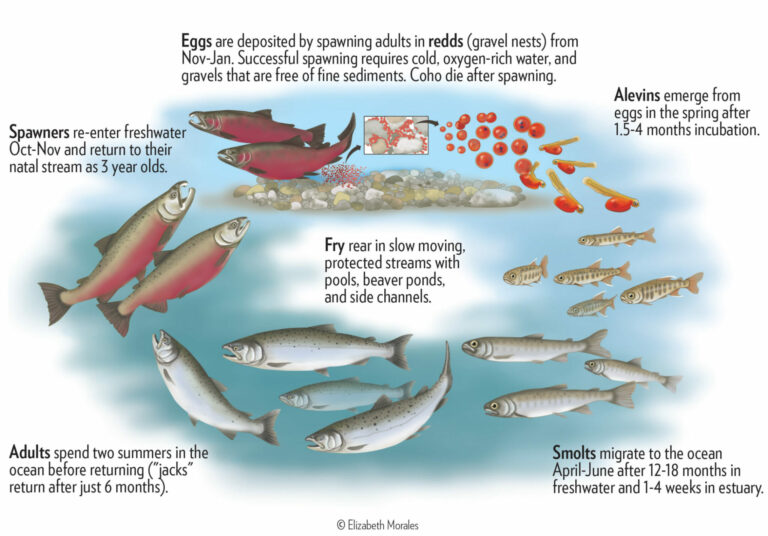
The use of wastewater in aquaculture has garnered attention as a sustainable practice that can contribute to food security while addressing waste management issues. Here’s an overview of its key aspects:
Benefits of Using Wastewater in Aquaculture
1. Nutrient Recycling: Wastewater often contains nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which can be beneficial for the growth of aquatic organisms. By utilizing these nutrients, aquaculture systems can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: Using wastewater can lower production costs for aquaculture farms by providing a free or low-cost source of nutrients, especially in areas where freshwater resources are scarce.
3. Environmental Impact: Recycling wastewater can help mitigate pollution by preventing the discharge of untreated wastewater into natural water bodies, thus protecting aquatic ecosystems.
4. Sustainable Water Use: In regions with water scarcity, reusing wastewater can help sustain aquaculture operations without depleting freshwater resources.
5. Integrated Systems: Wastewater aquaculture can be part of integrated farming systems, where the byproducts of one process serve as inputs for another. For example, fish farming can be combined with vegetable farming, where nutrient-rich water from fish tanks is used to irrigate crops.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Contaminant Levels: Wastewater may contain pathogens, heavy metals, or other pollutants that can harm aquatic life or accumulate in food chains. Proper treatment and monitoring are essential.
2. Water Quality Management: Maintaining optimal water quality in aquaculture systems is crucial. This includes managing pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and harmful substances.
3. Regulatory Frameworks: The use of wastewater in aquaculture is subject to regulations to ensure safety and environmental protection. Compliance with these regulations is essential for successful implementation.
4. Public Perception: There may be resistance from consumers regarding the use of wastewater in food production, necessitating education and awareness campaigns.
Practical Applications
• Fish Farming: Wastewater can be treated and used in fish farming, where species like tilapia or catfish are commonly raised in nutrient-rich environments.
• Aquaponics: This system combines aquaculture with hydroponics, where fish waste provides organic nutrients for plants, and plants help filter and purify the water for fish.
• Phytoremediation: Some aquatic plants can absorb contaminants from wastewater, allowing for bioremediation while simultaneously producing biomass for aquaculture.
Thank you for reading. Don't forget to subscribe & share!