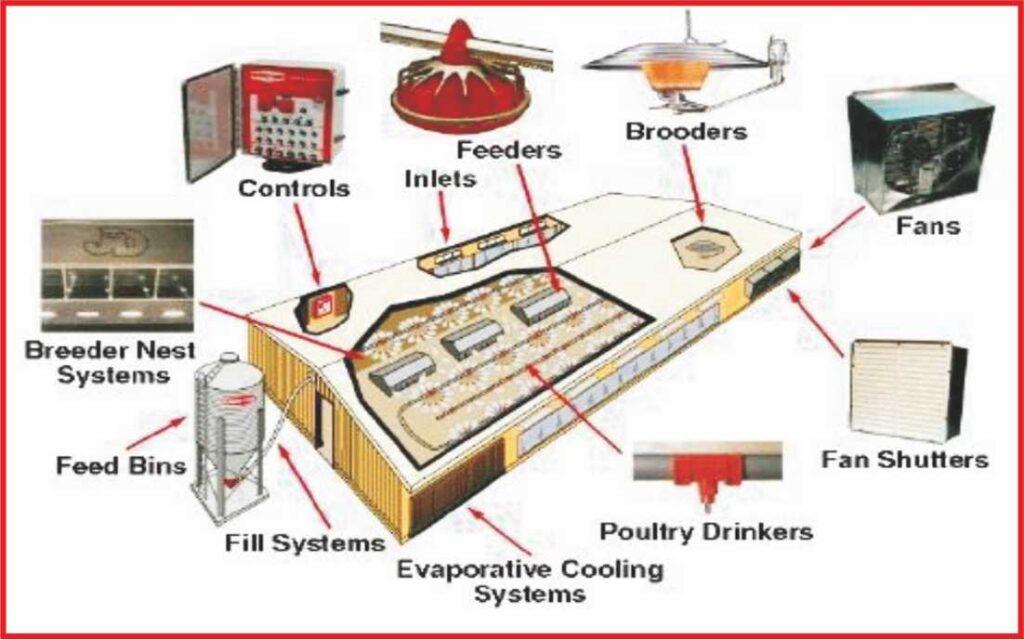
1. Precision Nutrition and AI-Driven Feed Formulation
- What it is: Use of artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and precision algorithms to tailor diets to the specific breed, age, and health status of poultry.
- Impact: Optimizes nutrient delivery, reduces waste, improves growth rates, and lowers feed cost.
- Example: Cloud-based nutrition platforms (e.g., Evonik’s AMINONIR® Live) analyze amino acid profiles in real-time.
2. Nanotechnology in Poultry Feed
- What it is: Incorporation of nano-minerals (e.g., nano zinc, selenium, and copper), nano-encapsulated vitamins, and phytogenics.
- Impact: Enhances nutrient absorption, improves immune response, and reduces feed-to-growth ratio.
- Example: Nano-selenium improves antioxidant status and reproductive health in layers and broilers.
3. Enzyme Technology and Customized Enzyme Cocktails
- What it is: Use of tailor-made enzymes (e.g., xylanases, phytases, proteases) to enhance digestion of complex ingredients.
- Impact: Improves nutrient utilization, especially in plant-based diets, and reduces excretion of phosphorus and nitrogen.
- Innovation: Use of heat-stable enzymes and multi-enzyme blends based on feed ingredients.
4. Microbiome Modulation and Gut Health Enhancers
- What it is: Use of precision probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics to improve gut microbiota.
- Impact: Enhances nutrient absorption, reduces pathogens, and boosts immunity.
- Innovation: Next-gen probiotics (e.g., spore-forming Bacillus species), metabolite-rich postbiotics, and microbiota sequencing for individualized gut support.
5. Sustainable Alternative Proteins
- What it is: Inclusion of novel proteins like insect meal (e.g., black soldier fly larvae), algae, yeast, and fermented soy.
- Impact: Reduces reliance on soybean and fish meal; supports circular agriculture and sustainability.
- Trend: EU, US, and China are investing in commercial-scale insect meal production for poultry feed.
6. Thermal Stress Nutrition Management
- What it is: Formulation of feed additives (e.g., betaine, chromium, and electrolytes) to counter heat stress.
- Impact: Maintains performance and egg production in tropical and arid climates.
- Innovation: Use of heat-tolerant strains and antioxidant-rich diets during high ambient temperature periods.
7. Smart Sensors and Digital Feed Monitoring
- What it is: Integration of sensors and IoT devices in poultry sheds to monitor feed intake, water usage, and growth metrics.
- Impact: Enables real-time feed adjustments, early detection of anomalies, and improved feed efficiency.
- Example: Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) systems.
8. Feed Additives as Antibiotic Alternatives
- What it is: Use of natural additives such as essential oils, organic acids, tannins, and peptides to replace antibiotics.
- Impact: Promotes gut health, improves growth, and meets consumer demand for antibiotic-free meat.
- Example: Encapsulated phytogenics with targeted release in the gut.
9. Conclusion:
Global poultry nutrition is moving towards precision, sustainability, and biosecurity. The integration of smart technologies, functional feed ingredients, and microbiome science not only enhances productivity but also addresses environmental and food safety concerns.
Thank you for reading. Don't forget to subscribe & share!