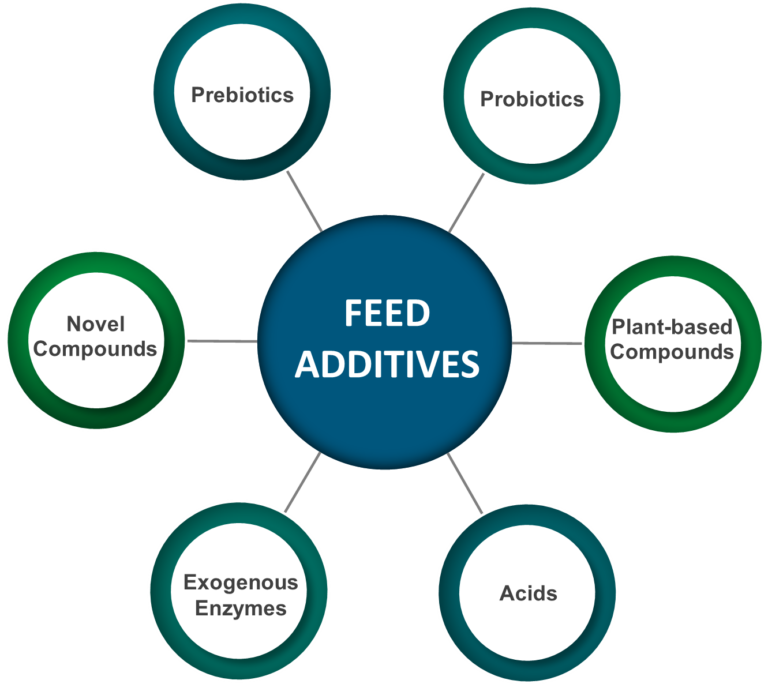
Feed additives are non-nutritive substances included in poultry diets to improve productivity, health, feed efficiency, and egg quality. In layer production, where both bird performance and product quality directly affect profitability, feed additives play a crucial role in achieving optimal outcomes. They serve multiple functions, ranging from nutrient utilization to disease prevention and egg enrichment. The following are the major roles of feed additives in layer feeds:
Thank you for reading. Don't forget to subscribe & share!
- Improvement of Digestibility and Feed Efficiency
Enzymes (e.g., phytase, xylanase, β-glucanase) break down anti-nutritional factors and enhance the utilization of energy, protein, and phosphorus. This leads to a better feed conversion ratio (FCR) and reduces feed cost per dozen eggs. Enhanced nutrient absorption also minimizes undigested feed waste, reducing environmental impact.
- Maintenance of Gut Health and Microbial Balance
Probiotics (live beneficial microbes) and prebiotics (non-digestible feed ingredients that promote beneficial bacteria) improve intestinal microbial balance. They suppress pathogenic organisms like Salmonella and E. coli, reducing disease incidence. Organic acids (formic, lactic, citric acids) lower gut pH, improving digestion and controlling harmful bacteria.
- Enhancement of Egg Production and Quality
Vitamins and minerals (especially vitamin D3, calcium, phosphorus, manganese, zinc) are crucial for eggshell formation and strength. Pigments (xanthophylls, carotenoids) enhance yolk color, an important quality parameter in commercial markets. Omega-3 fatty acid supplements (fish oil, flaxseed oil) enrich egg yolk with health-promoting nutrients for consumers.
- Improvement of Immunity and Disease Resistance
Immunostimulants like β-glucans and yeast extracts improve natural immunity, reducing dependence on antibiotics. Herbal extracts and essential oils (oregano, garlic, thyme) act as natural antimicrobials and antioxidants. Toxin binders neutralize mycotoxins in contaminated feed, preventing immunosuppression and organ damage.
- Stress Management in Layers
Layers are highly sensitive to heat, cold, transport, and handling stress, which can lower production. Electrolytes and vitamins (C, E) help birds cope with oxidative stress, especially during hot weather. Adaptogens like herbal extracts (e.g., ashwagandha) support resilience under stress conditions.
- Prolonging Egg Shelf Life and Safety
Antioxidants (vitamin E, selenium, BHT, BHA) protect lipids in feed and eggs from oxidation, ensuring better storage quality. Reduced lipid peroxidation also maintains consumer acceptability of eggs. Certain additives improve egg microbial safety by reducing pathogen load.
- Economic and Environmental Benefits
Efficient use of nutrients through feed additives lowers feed costs—the most expensive input in egg production. Reduction of nitrogen and phosphorus excretion through enzyme supplementation minimizes environmental pollution. Sustainable egg production becomes more feasible with additive technology.
- Supposition
Feed additives in layer diets are not merely optional supplements but strategic tools to optimize performance, egg quality, bird health, and economic returns. Their judicious and science-based use ensures sustainable production, enhances food safety, and supports consumer demand for high-quality, functional eggs.