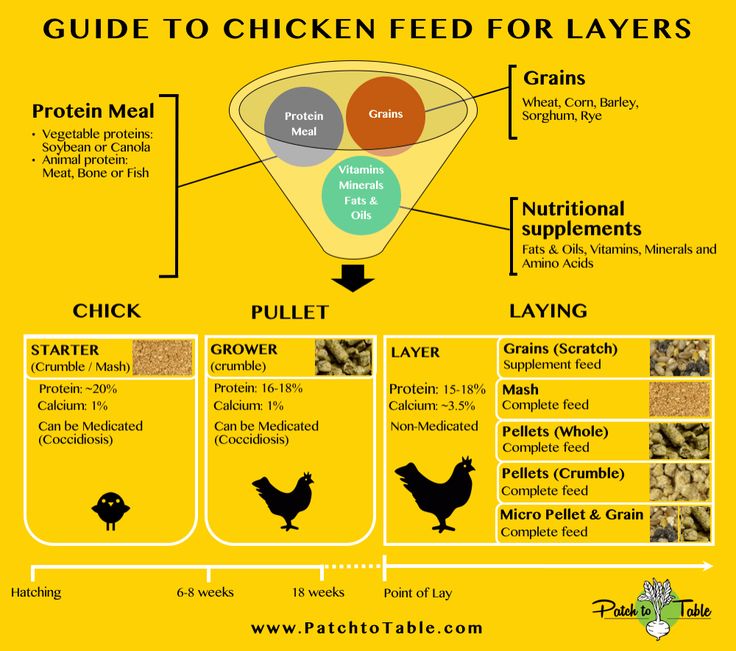
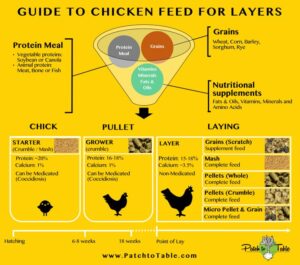
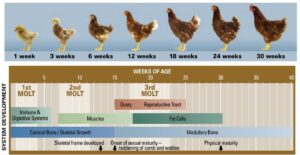
Types of Layer Feeds
- Starter Feed (0–6 weeks): High protein (18–20%) and balanced amino acids to support rapid growth.
- Grower Feed (7–18 weeks): Moderate protein (15–17%), controlled energy to prevent obesity, and adequate minerals for skeletal development.
- Pre-Layer Feed (18–20 weeks): Transition diet with higher calcium (2–2.5%) to prepare pullets for egg production.
- Layer Feed (20 weeks onward): High calcium (3.5–4.5%), balanced phosphorus, adequate protein (16–18%), vitamins, and trace minerals to support sustained egg production and eggshell quality.
Nutrient Evaluation
- Protein and Amino Acids: Lysine and methionine are critical for egg production.
- Energy Levels: ME (Metabolizable Energy) balance ensures proper body weight and egg mass production.
- Minerals: Calcium and phosphorus ratio is crucial for shell strength.
- Vitamins: Vitamin D3 for calcium absorption, A and E for immunity, and B-complex for metabolism.
Feed Formulations
- Mash Feed: Simple ground mixture; good for small farms but may cause selective feeding.
- Pelleted Feed: Improves feed intake, reduces wastage, and ensures nutrient uniformity.
- Crumble Feed: Easier for younger birds to consume during transition stages.
Evaluation Methods
- Performance Indicators: Egg production rate, egg weight, feed conversion ratio (FCR), body weight, and mortality.
- Egg Quality Parameters: Shell thickness, yolk color, Haugh unit (albumen quality).
- Economic Evaluation: Cost per kg feed, feed efficiency, cost per dozen eggs.
- Health Indicators: Bone strength, feather condition, and immunity response.
5. Practical Considerations
- Feed must be formulated according to climate (heat stress), housing system (cage vs. free-range), and bird strain requirements.
- Seasonal adjustments (e.g., electrolytes and antioxidants in hot climates) are important.
- Alternative feed ingredients (e.g., agro-industrial by-products) are being tested to reduce feed costs.
In summary: Evaluation of layer feeds involves assessing nutritional adequacy, feed form, performance outcomes, egg quality, economic viability, and adaptability to local farming systems.
Thank you for reading. Don't forget to subscribe & share!