Blogs

Theories of continental drift and plate tectonics
Theory of Continental Drift: Proposed by: Alfred Wegener (1912)Wegener, a German meteorologist and geophysicist, proposed that continents were once a single landmass that drifted apart over geological time.The Supercontinent – Pangaea. Around 300 million years ago, all landmasses were joined together in a supercontinent called Pangaea.Pangaea later broke into two major landmasses: Laurasia (North America,…
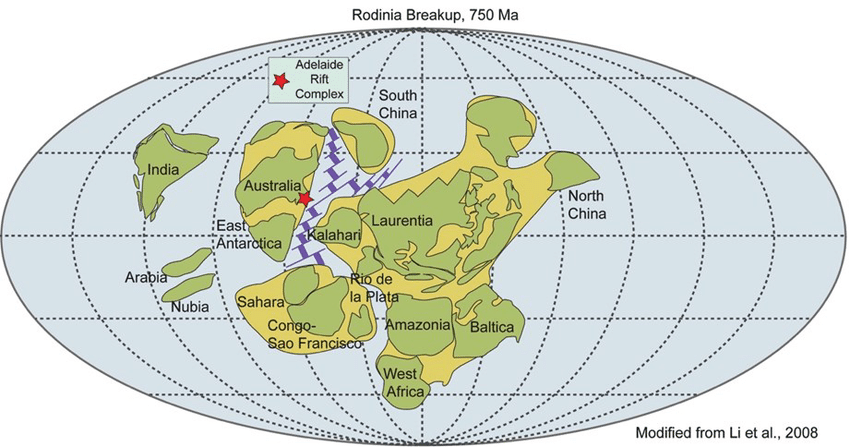
Palaeogeography
Palaeogeography is the branch of geology that reconstructs the historical geography of Earth’s surface. It seeks to understand how continents, oceans, mountain ranges, and other geographic features have changed position and form over geological time. By combining data from sedimentology, paleontology, stratigraphy, tectonics, and geochronology, Foundations of Palaeogeography The foundation of palaeogeography lies in the…
Neotropical Realm, Ethiopian Realm, Oriental Realm & Australian Realm
Neotropical Realm A. Geographical Boundaries:The Neotropical Realm includes South and Central America, the lower part of Mexico, and the West Indies. It is connected to the Nearctic Realm via the Central American Isthmus, while its other boundaries are defined by surrounding seas. B. Subdivisions:This realm is divided into four sub-regions: C. Climatic Conditions: Most of…
Map work for identification of various zoogeographical regions of the world
Zoogeography is the branch of biogeography that deals with the distribution of animal species and populations across geographical areas of the Earth. The world is traditionally divided into six major zoogeographical (faunal) regions, each with its unique assemblage of fauna due to historical isolation, climate, and evolutionary factors. Major Zoogeographical Regions Palaearctic Region Nearctic Region…
Study and Identification of Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks
Rocks are naturally occurring aggregates of minerals and are classified into three main types based on their formation processes: Igneous Rocks – Formed from the solidification of molten magma or lava. Sedimentary Rocks – Formed from the accumulation and lithification of sediment. Metamorphic Rocks – Formed when existing rocks are altered by heat, pressure, or…
Study of Vertebrate Fossils: Horse, Elephant, Camel, and Bovids
Vertebrate paleontology involves the study of fossilized bones, teeth, and traces of animals with backbones. Fossils of large mammals such as horses, elephants, camels, and bovids (cattle-like animals) are key to understanding evolutionary processes, climatic shifts, and faunal dispersal across geologic time. These animals, part of the order Ungulata (hoofed mammals), are particularly valuable for…
Study of invertebrate fossils of coelenterates, trilobites, ammonite, brachiopods, mollusks and echinoderms
Invertebrate fossils form a substantial part of the fossil record and are key indicators in the fields of paleontology, biostratigraphy, and evolutionary biology. These organisms, lacking vertebral columns, often had hard shells or exoskeletons which fossilized well. Their abundance and widespread distribution make them excellent index fossils for dating sedimentary rock layers. 1. Coelenterates (Cnidarians):…
Study of Fauna of mould, cast, pseudomorph, corprolite, petrified fossils of plants and animals
Fossils are preserved remains, impressions, or traces of organisms from the remote past, usually embedded in sedimentary rocks. Fossilization is a rare process that involves chemical and physical changes over millions of years. Different types of fossilization processes result in various fossil forms, including moulds, casts, pseudomorphs, coprolites, and petrified fossils. Studying these forms provides…
Study of Fauna of various zoogeographical regions
The Earth’s biodiversity is not uniformly distributed. Instead, it varies geographically due to climatic, evolutionary, geological, and ecological factors. To study and understand these variations, the world is divided into distinct zoogeographical regions, each with its unique fauna (animal life). The concept was first proposed by Philip Lutley Sclater (1857), and later refined by Alfred…
International code of zoological nomenclature; its objective, principles, interpretation, application of important rules, with reference to Zoological nomenclature, law of priority and validity of names
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) provides a universal set of rules and recommendations for naming animals. It ensures that every animal species has one correct and universally accepted scientific name. The ICZN promotes stability, clarity, and universality in animal names. Objectives of ICZN: To standardize zoological names globally. To ensure stability and universality…
Taxonomic Keys: different kinds of keys and their merits and demerits
Taxonomic Keys: different kinds of keys and their merits and demerits Taxonomic Keys: A taxonomic key is a tool used by scientists to identify organisms based on a series of choices that lead to the correct name of a given item. Keys are structured as a step-by-step process where at each step, you select between…