Introduction
Bio-assaying is a biological testing technique used to quantify the potency or bioavailability of nutrients in feeds by observing their physiological effects on living organisms—typically poultry birds in animal nutrition studies. It helps in determining how much of a nutrient in a feedstuff is biologically active, absorbable, and usable by the bird, especially when chemical analysis alone cannot provide complete nutritional value.
Objectives of Bio-assays in Poultry
- To determine nutrient availability (e.g., vitamins, minerals, amino acids).
- To assess the biological efficiency of feed additives or supplements.
- To compare the effectiveness of natural vs. synthetic nutrient sources.
- To establish nutritional standards or requirements for poultry.
Types of Bio-assays
- Growth Assays
- Measure weight gain, feed intake, and feed conversion ratio (FCR) in response to different levels of a test nutrient.
- Commonly used for amino acids (e.g., lysine, methionine) and energy evaluation.
- Metabolism Assays
- Monitor nutrient absorption, retention, and excretion.
- Useful for minerals and trace elements (e.g., calcium, phosphorus, zinc).
- Tissue or Organ Response Assays
- Measure biochemical markers or organ weights (e.g., liver vitamin concentration for vitamin assays).
- Reflects nutrient functionality at the cellular level.
- Blood Parameter Assays
- Nutrient levels in blood or enzymatic activity (e.g., alkaline phosphatase for phosphorus).
- Non-invasive and effective for monitoring mineral and vitamin status.
- Egg Production and Quality Assays
- In laying hens, bio-assays may include egg weight, shell quality, and yolk color.
- Often used to test the availability of calcium, vitamin D, and pigments.
Typical Bio-assay Design
- Experimental Groups: Birds are divided into multiple groups with varying levels of the test nutrient (including a control and a positive standard).
- Replication: Multiple replicates per treatment ensure statistical reliability.
- Duration: Typically 3 to 6 weeks depending on the nutrient and physiological response.
- Measurements:
- Body weight gain
- Feed intake
- Feed efficiency
- Blood/tissue nutrient levels
- Specific organ weights or histological assessments
Key Nutrients Commonly Bio-assayed in Poultry
| Nutrient | Measured Effect/Response |
|---|---|
| Lysine, Methionine | Growth rate, feed efficiency |
| Vitamin A | Epithelial health, eye lesions |
| Vitamin D3 | Bone development, calcium retention |
| Zinc | Feathering, immune response |
| Phosphorus | Bone strength, phosphorus excretion |
| Selenium | Antioxidant enzyme activity (e.g., glutathione peroxidase) |
Advantages of Bio-assaying in Poultry
- Reflects actual biological utilization rather than total nutrient content.
- Provides insight into interactions among nutrients (e.g., Ca:P ratio).
- Essential for validating novel feed ingredients or alternative feed sources.
Limitations
- Requires careful experimental design and controlled environments.
- Can be time-consuming and costly.
- Biological variability among birds may influence results.
- May not isolate effects of a single nutrient unless other dietary components are strictly controlled.
Conclusion
Bio-assaying is a powerful tool in poultry nutrition to evaluate the bioavailability and efficacy of nutrients in feed. It goes beyond chemical composition, offering valuable data for feed formulation, nutrient requirement determination, and performance optimization. With the rise of alternative feed ingredients and functional additives, bio-assays remain crucial for ensuring safe and effective poultry diets.


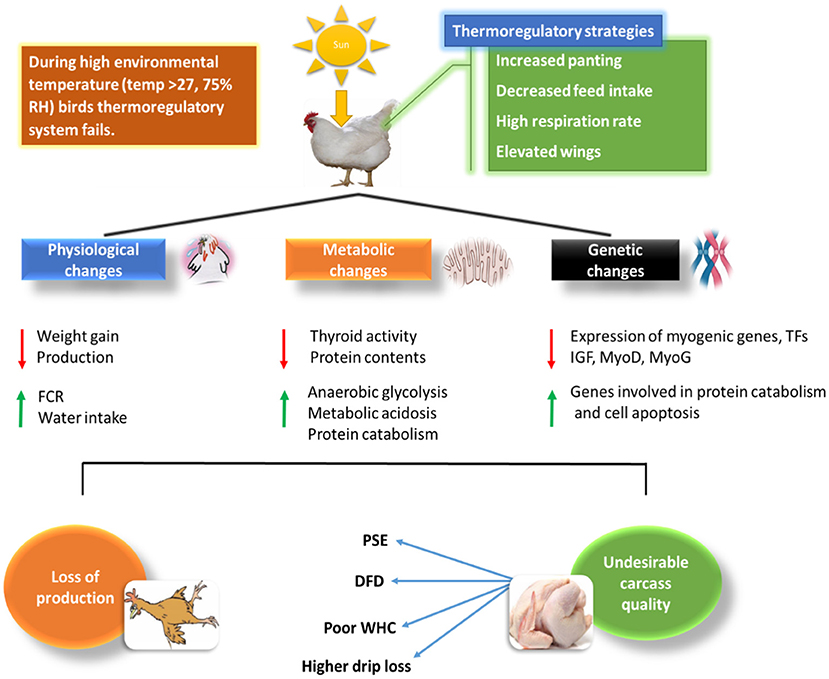
very informative for research of different ingredient on bird
Very informative about nutrients and their effect on birds
Highly informative,
Very informative about poultry nutrition and feed conversation ratio
Knowledge full for our research in nutrition courses
Effective and practical information
Knowledge full for our research in nutrition courses
Highly informative